GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication) is open digital cellular technology used for transmitting voice and providing data services.
GSM supports voice traffic as well as data traffic in form of CSD (Circuit switched data) or HSCSD (High speed circuit switched data).
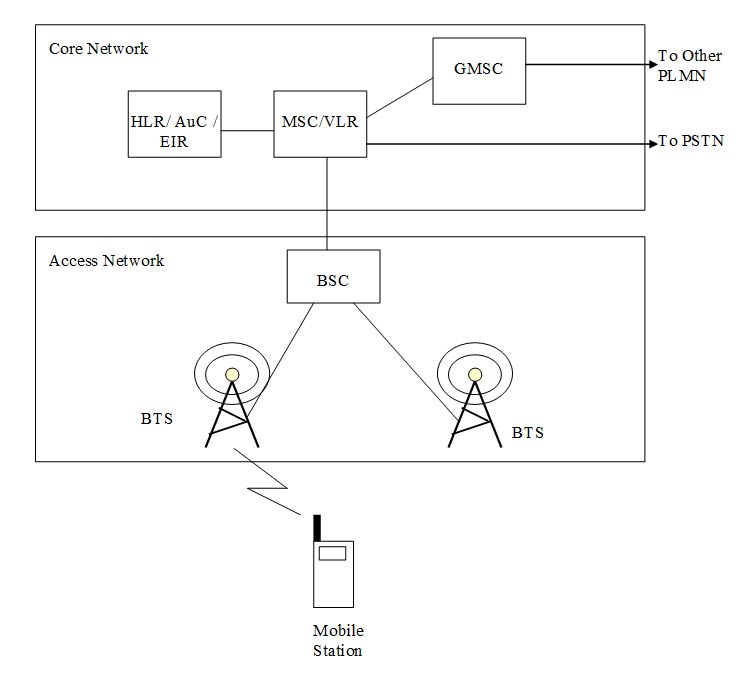
Network Architecture
GSM network is logically divided in two parts Access network (AN) and Core Network (CN). Access network deals with communication of Mobile handset with the network over radio interface and Core networks deals with routing of the call within same network or to another network like PSTN.
Network Architecture for GSM is hierarchical i.e. 1 BSC (Base station controller) handles multiple BTS (Base Transceiver Station), 1 MSC (Mobile-service switching centre) handles multiple BSC.
Various entities and their functionality is described in following section
- Core Netowrk
- MSC (Mobile-service switching centre):MSC acts as interface between radio network and fixed network. MSC acts as exchange which performs all switching and signalling functions for mobile stations located in MSC area i.e. MS attached to one of the BTS handled by particular MSC. MSC is also responsible for location registration and handover procedures for mobile stations.
- VLR (Visitor Location Register): A mobile station roaming in an MSC area is controlled by the Visitor Location Register in charge of this area. When a Mobile Station (MS) enters a new location area it starts a registration procedure. The MSC in charge of that area notices this registration and transfers to the Visitor Location Register the identity of the location area where the MS is situated. If this MS is no yet registered, the VLR and the HLR exchange information to allow the proper handling of calls involving the MS. A VLR may be in charge of one or several MSC areas.
- HLR(Home Location Register): This functional entity is a data base in charge of the management of mobile subscribers. A PLMN may contain one or several HLRs: it depends on the number of mobile subscribers, on the capacity of the equipment and on the organisation of the network. The following kinds of information are stored there:
- the subscription information;
- some location information enabling the charging and routing of calls towards the MSC where the MS is registered(e.g. the MS Roaming Number, the VLR Number, the MSC Number, the Local MS Identity).
- AuC(Authentication Centre): AuC is associated with an HLR, and stores an identity key for each mobile subscriber registered with the associated HLR. This key is used to generate:
- data which are used to authenticate the International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI);
- a key used to cipher communication over the radio path between the mobile station and the network.
- EIR(Equipment Identity Register): This functional entity contains one or several databases which store(s) the IMEIs used in the GSM system.The mobile equipment may be classified as “white listed”, “grey listed” and “black listed” and therefore may be stored in three separate lists.
- GMSC(Gateway MSC): If a network, delivering a call to the PLMN cannot interrogate the HLR, the call is routed to an MSC. This MSC will interrogate the appropriate HLR and then route the call to the MSC where the mobile station is located. The MSC which performs the routing function to the actual location of the MS is called the Gateway MSC (GMSC).
- Access Network
- BTS(Base Transceiver Station): A BTS is a network component which serves one cell. BTS is responsible for communication over radio interface with Mobile Station.
- BSC(Base Station Controller): A BSC is a network component in the PLMN with the functions for control of one or more BTS. BSC is responsible for radio resource management and handovers of mobile station from BTS to BTS.
Radio Frequency Bands
Frequency bands used by GSM are as follows
| T-GSM 380 band | 380,2 MHz to 389,8 MHz: Uplink 390,2 MHz to 399,8 MHz Downlink |
| T-GSM 410 band | 410,2 MHz to 419,8 MHz: Uplink 420,2 MHz to 429,8 MHz Downlink |
| GSM 450 band | 450,4 – 457,6 MHz: Uplink 460,4 – 467,6 MHz: Downlink |
| GSM 480 band | 478,8 – 486 MHz: Uplink 488,8 – 496 MHz: Downlink |
| GSM 710 band | 728 – 746 MHz: Downlink 698 – 716 MHz: Uplink |
| GSM 750 band | 777 – 793 MHz: Uplink 747 – 763 MHz: Downlink |
| T-GSM 810 band | 806 – 821 MHz: Uplink 851 – 866 MHz: Downlink |
| GSM 850 band | 824 – 849 MHz: Uplink 869 – 894 MHz: Downlink |
| Primary GSM 900 band | 890 915 MHz: Uplink 935 960 MHz: Downlink |
| E-GSM 900 band | 880 915 MHz: Uplink 925 960 MHz: Downlink |
| R-GSM 900 band | 876 915 MHz: Uplink 921 960 MHz: Downlink |
| DCS 1800 band | 1710-1785 MHz: Uplink 1805-1880 MHz: Downlink |
| PCS 1900 band | 1850-1910 MHz: Uplink 1930-1990 MHz: Downlink |
RF channel spacing in GSM is 200 kHz, allowing for 41 (T-GSM 380), 41 (T-GSM 410), 35 (GSM 450), 35 (GSM 480), 89 (GSM 710), 74 (GSM 750), 74 (T-GSM 810), 124 (GSM 850), 194 (GSM 900), 374 (DCS 1 800) and 299 (PCS 1900) radio frequency channels, thus leaving a guard band of 200 kHz at each end of the sub-bands.
Interfaces and Protocols
- Um Interface
- LAPDm
- Abis Interface
- RR
- LAPD
- A Interface
- BSSMAP
- SCCP
- MTP
- CC
- MM
- CM
- B Interface
- C Interface
- MAP/C
- SCCP
- MTP
- D Interface
- MAP/D
- SCCP
- MTP
- E Interface
- MAP/E
- SCCP
- MTP
- F Interface
- MAP/F
- SCCP
- MTP
- G Interface
- MAP/G
- SCCP
- MTP
References
[1] 03.02 Cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Network architecture
[2] 23.002 Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Network architecture
[3] 45001 Technical Specification Group GSM/EDGE Radio Access Network; Physical layer on the radio path; General description

Permalink
Great article. Thanks for sharing