The idea of IMS is old, but after it’s deployment with LTE users and operators can harness the true power of IMS.
IMS – IP Multimedia Subsystem is a standalone system. It resides out of the LTE network and connected to PDN Gateway through SGi interface.
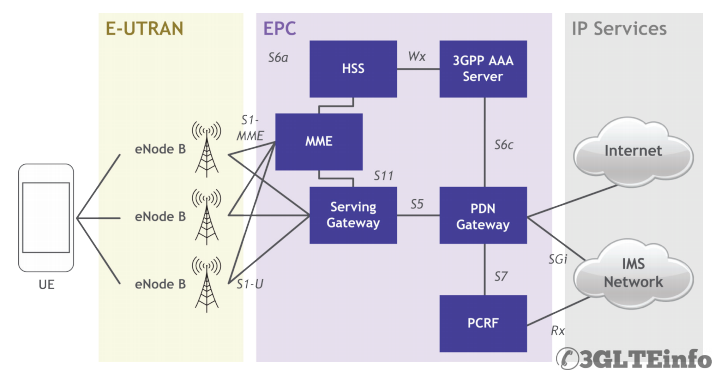
The EPC has three main functional elements.
- The first one is Mobility Management Entity (MME). MME is the single most control point in the EPC and responsible for most of the control plane functions.
- The second in the list is Serving Gateway (S-GW). All IP packets in uplink and downlink flow through S-GW. S-GW is also responsible for handling handovers.
- The last in the list is P-GW or PDN Gateway. P-GW allocates IP addresses to UEs. It also provides interfaces towards internet and IMS.
The following architecture diagram shows EPC, IMS and the interface between them.
User Equipment (UE)
UE is a mobile terminal authorized to be used in an LTE network. UE may be a smartphone, tablet or other communication devices.
An IMS powered UE has two main components.
- Universal Integrated Circuit Card (UICC)
- Session Initiation Protocol User Agent (SIP UA)
Universal Integrated Circuit (UICC)
Each UE must contain one UICC and each UICC may have one or more of the following modules.
- Subscriber Identity Module (SIM): SIM identity information used by a GSM network.
- UMTS Subscriber Identity Module (USIM): USIM information used by a UMTS or LTE network.
- CDMA Subscriber Identity Module (CSIM) or Re-Useable Identification Module (R-UIM). CDMA network uses this identity information
- IP Multimedia Services Identity Module (ISIM): IMS subsystem uses IMSI identity information.
Let’s look into ISIM which is important when UE wants to use IMS resources in the network. ISIM contains the following:
- IP Multimedia Private Identity (IMPI): IMPI is a global identity allocated by the home network. IMPI contains home operator’s domain information.
- Home operator’s domain name
- IP Multimedia Public Identity (IMPU): IMPU acts like a telephone number. It can either be a SIP URI (sip:
@ : ) or a tel URI. Definition of tel URI from RFC 39664 (tel: ). - Secret Key: This long secret key is used for user authentication and SIP registration.
SIP User Agent (SIP-UA)
SIP User Agent resides in the UE to send and receive SIP messages. SIP-UA provides basic telephony functionality. It can act in two different roles:
- User Agent Client (UAC): As a client to send SIP request
- User Agent Server (UAS): As a server to receive requests and send response
Evolved Packet Core (EPC)
For VoLTE and IMS prospective two nodes are important in the Evolved Packet Core.
Public Data Network Gateway (PDN-GW)
PDN Gateway allocates IP addresses to UEs. PDN-GW is also the point of communication between EUTRA and non-3GPP services like the internet.
When IMS is available, there can be more that one PDN-GW in the EPC, one for internet and one for IMS.
Policy and Charging Rule Function (PCRF)
The PCRF determines the allowed traffic types in real-time. It also checks how to account for the traffic. Operators use this information for billing purpose.
Based on requests for IMS services, the PCRF also initiates the appropriate bearers.
When a UE starts a VoLTE call, the PCRF checks if the UE has a subscription to start VoLTE call. If the UE has VoLTE subscription, PCRF setup dedicated bearer for IMS services.
IMS Core
IMS core handles session management and media control.

IMS core has the following important nodes.
Call Session Control Function (CSCF)
CSCF establishes monitors, supports, and releases multimedia sessions. It has three different functional elements. These may or may not be separate physical entities.
- Proxy CSCF: P-CSCF acts as the initial point of contact from any SIP User Agent. It handles all requests from the UE and is, from the UE’s point of view, the “SIP proxy” to the entire subsystem.
- Serving CSCF: S-CSCF has knowledge about the user and what applications are available to the user. It acts as a decision point. S-CSCF’s main job is to decide whether the user’s SIP messages will be forwarded to the application servers.
- Interrogating CSCF: I-CSCF is the entity that initiates the assignment of a user to an S-CSCF (by querying the HSS) during registration.
Home Subscriber Server (HSS)
HSS is a database that maintains user profiles and location information. It handles name and address resolution. HSS is also responsible for authentication and authorization.
Subscriber Location Function (SLF)
SLF assigns HSS to a user in the home network. To achieve this function SLF keeps track of all HSS.
Media Gateways
Media Gateway resides at the interface between SIP-based IMS network and traditional PSTN network.
You can find more details in RFC 3372.
RFC 3372 – Session Initiation Protocol for Telephones (SIP-T): Context and Architectures
Media Gateway Control Function(MGCF)
MGCF controls media gateways and converts codecs where necessary. Also, it may serve as a breakout to a circuit-switched network.
When MGCF works as a breakout to CS network, it is also responsible for:
- managing the conversion of signaling messages,
- converting SIP messaging to the Bearer Independent Call Control (BICC) and,
- ISDN User Part (ISUP) protocols used in legacy systems.
Breakout Gateway Control Function (BGCF)
When MGCF does not include breakout to CS network, BGCF takes care of this functionality.

Permalink
This seems a bit confused to me; if you are trying to show one operator’s network why would they maintain a separate HSS for the EPC and the IMS? A primary point of IMS (granted not always realised in practise) is service convergence.
Permalink
I want to know whether Voice will consume Data in Volte or Not?
Permalink
Hi sir
How can I enable volte on my Nexus 6p phone with jio sim
After dialling *#*#4636#*#* I got this under IMS
IMS registeration :not registered
Voice over LTE. : Unavailable
Voice over WiFi. : Unavailable
Video calling. : Unavailable
Ut interface. : Unavailable
Please guide
Permalink
Voice in Volte does not consume Data.
Voice services use a dedicated bearer apart from Data PDN.
For commercial networks, voice services and data services use the different bearers.
Permalink
Thank you for taking the time to share this information. Its very helpful.