SRNS relocation is a procedure used during mobility scenarios when Control of the Serving Radio Network Subsystem (SRNS) is changed to another Radio Network Subsystem (RNS)
Radio Network Subsystem (RNS): The RNS controls the allocation and release of radio resources to establish a connection between a UE and the UTRAN.
A single UE may be associated with one or more Radio Access Bearers (RABs). For instance a UE may simultaneously use one RAB for voice and one RAB for a packet call.
Radio Access Bearer (RAB): RAB is a logical connection between the UE and the UMSC/SGSN.
Iu Bearer: The connection between the RNC and the Core network is referred to as the Iu bearer.
Radio Bearer (RB): The connection between the RNC and the UE is referred to as the Radio Bearer (RB).
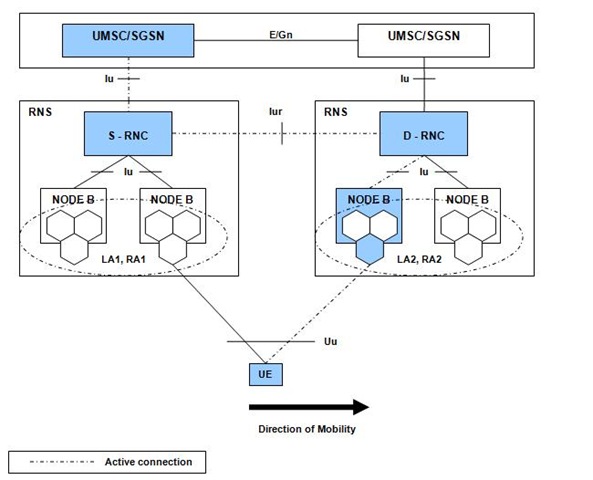
During Hard Handover when the UE moves away from the area that is covered by one RNS to a new RNS, there is a requirement to perform an inter-RNC handover between the Serving RNC (S-RNC) to the Target RNC (RNCT) of the new RNS.
There are two ways to change the Serving RNC:
- One possibility is that the Target RNC may immediately become the Serving RNC referred as the Combined Hard Handover and SRNS Relocation Procedure
- In the other case known as the Serving RNS Relocation Procedure the user plane from the S-RNC extends to the Target RNC, in this situation the Target RNC is referred as the Drift RNC. The Interface between the Serving and the Drift RNC is the Iur interface described in the 3GPP TS 25.420.
NOTE: In either case the Serving RNC initiates the SRNS relocation procedure.
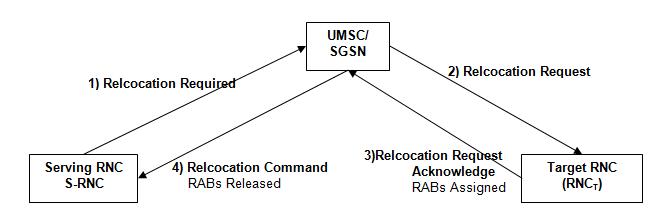
Relocation Procedure
| RELOCATION REQUIRED | RELOCATION REQUEST |
| Information Element | Information Element |
|
|
| RAB to be Setup | |
|
Serving RNS Relocation Procedure
This procedure is only performed for a UE in CONNECTED state where the Iur interface carries both the control signaling and the user data.
The Serving SRNS Relocation procedure is used to move the connection between the RAN and the CN for the source SRNC to the RAN for the target RNC, from a "standing still position". In the procedure, the Iu links are relocated.
If the target RNC is connected to the same SGSN as the source SRNC, an Intra-SGSN SRNS Relocation procedure is performed.
If the routing area is changed, this procedure is followed by an Intra-SGSN Routing Area Update procedure. The SGSN detects an Intra-SGSN routing area update by noticing that it also handles the old RA. In this case, the SGSN has the necessary information about the UE and there is no need to inform the HLR about new location of the UE.
Before the SRNS Relocation procedure and RA update, the UE is registered in the old SGSN. The source RNC is acting as a serving RNC (SRNC).
Serving SRNS Relocation procedure Signalling
NOTE: The sequence is valid for both intra-SGSN SRNS relocation and inter-SGSN SRNS relocation.

After the SRNS Relocation procedure and RA update, the UE is registered in the new SGSN. The UE is in the state CONNECTED Mode towards the new SGSN, and the target RNC is acting as the serving RNC.
Combined Hard Handover and SRNS Relocation Procedure
This procedure is only performed for an UE in CONNECTED state in case the Iur interface is not available.
The Combined Hard Handover and SRNS Relocation procedure is used to move the connection between the RAN and the CN for the source SRNC to the RAN for the target RNC, while performing a hard handover decided by the RAN.
In the procedure, the Iu links are relocated.
If the target RNC is connected to the same SGSN as the source SRNC, an Intra-SGSN SRNS Relocation procedure is performed.
If the routing area is changed, this procedure is followed by an Intra-SGSN Routing Area Update procedure. The SGSN detects that it is an intra-SGSN routing area update by noticing that it also handles the old RA. In this case, the SGSN has the necessary information about the UE and there is no need to inform the HLR about the new UE location.
If the target RNC is connected to a different SGSN than the source SRNC, an Inter-SGSN SRNS Relocation procedure is performed. This procedure is followed by an Inter-SGSN Routing Area Update procedure.
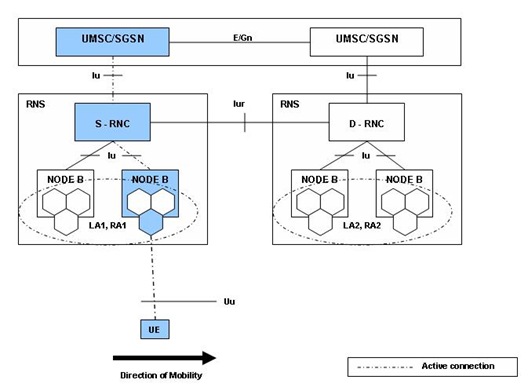
Before the SRNS Relocation and Routing Area Update the UE is registered in the old SGSN and in the old MSC/VLR. The source RNC is acting as serving RNC.
Combined Hard Handover and SRNS Relocation Procedure Signalling
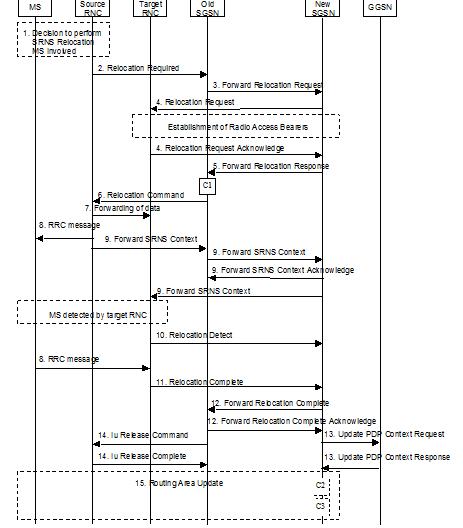
The sequence is valid for both intra-SGSN SRNS relocation and inter-SGSN SRNS relocation. Furthermore, this signaling flow is also applicable for BSS to RNS relocation and vice-versa, as well as BSS to BSS relocation.
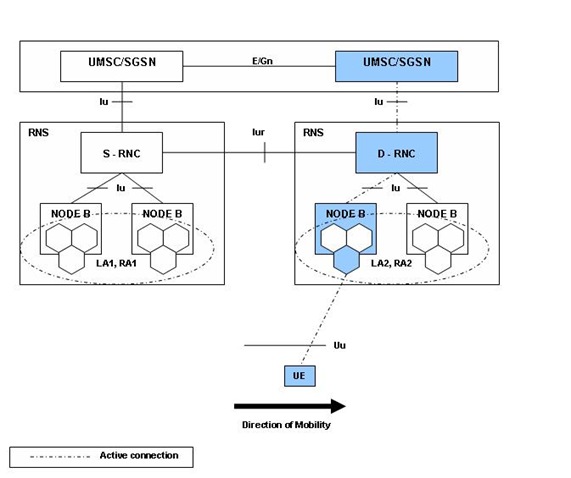
After the SRNS relocation and RA update, the UE is registered in the new SGSN and in the new MSC/VLR. The UE is in CONNECTED mode towards the new SGSN and in MM IDLE state towards the new MSC/VLR. The target RNC is acting as serving RNC.
References:
- UTRAN Iu interface RANAP signalling: 3GPP TS 25.413
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS);Service description;Stage 2: 3GPP TS 23.060
- SRNS relocation in a UMTS network: Patent US 6,807,419



Permalink
I’m not the type to take the time placing comments on peoples’ blogs normally however right after stumbling across yours I figured I’d shoot a quick line to give myself a break from working. I have definitely spent a bit of time here browsing and procrastinating! Keep up the great writing and i’m already looking towards checking out upcoming blog posts. Many thanks!
Permalink
I’m not the type to take the time placing comments on peoples’ blogs normally however right after stumbling across yours I figured I’d shoot a quick line to give myself a break from working. I have definitely spent a bit of time here browsing and procrastinating! Keep up the great writing and i’m already looking towards checking out upcoming blog posts. Many thanks!
Permalink
hello Sir,
My project is about simulating LTE RLC Layer in OMNeT++…i learnt that RLC layer’s functionality is same in both UE and enodeB, Is it right??? is there any difference in their functionality ???
thanks in advance…..
nagu
Permalink
Hi, I want to ask a question about Iu mode RA update procedure. In the TS123.060, page 113, it says “a new S4-SGSN indicates reserved TEID and IP address parameters from an SGW to an old Gn/Gp SGSN so that the old Gn/Gp SGSN can forward data packets when needed.” I am not very understand this procedure. I think the old SGSN will only send the data packets to new SGSN, why it will send the data to SGW?
Thanks so much!
Adrian
Permalink
Hi blogger, do you monetize your 3glteinfo.com ? There is easy method to earn decent money every month, just search on youtube : How to earn with wordai 4
Permalink
In Combined Hard Handover and SRNS Relocation Procedure Signalling, i feel step 7 is incorrect since there is no connection between source & target RNC. Source RNC should forward packets to old SGSN. Then old SGSN may forward packets to new SGSN which in turn may further send to new SRNS.After this step, Update PDP may happen between SGSN & GGSN.