This tutorial describe details of LTE CSBF : Circuit Switch Fall Back, which is essential for early adaptation of voice over LTE network.
LTE was made for packet based services. But a majority part of today’s traffic originates from CS based services like Voice and SMS. Therefore 3GPP agreed to include an intermediate solution for CS (Circuit Switch) based services until IP-based services like VoLTE completely developed and deployed. Using CSFB (CS Fallback) UE can switch to GERAN, UTRAN or CDMA2000 systems for voice services. CS fall back services are available in those areas where EUTRA systems overlap with GERAN, UTRAN or CDMA2000.
LTE CS Fallback Architecture
For CS Fallback Gs interface between MSC server and MME is required. ia SGs interface, the UE executes combined EPC and IMSI attachment and detachment procedure. Also for MT CS fallback service, CS paging is delivered via SGs interface to MME and ultimately to the UE. The SGs interface is based on the Gs interface.
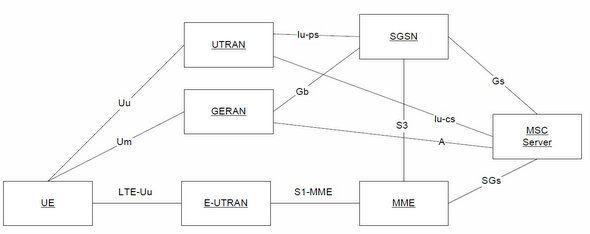
Though CS Fallback is a temporary solution till IMS based VoLTE is completely developed and deployed, but still CS Fallback is important for enabling an easy transition to 4G LTE
There are various solutions suggested for CS Fallback staring from Cell Change Order to target system, RRC Connections Release with redirection and RRC Connection release without redirection.
Listed here are various solutions suggested in different release
LTE CS fallback options in Release 8 and 9
- Target system Solutions Release UTRAN RRC Connection Release with Redirection without Sys Info Release 8
- RRC Connection Release with Redirection with Sys Info Release 9
- PS handover with DRB(s) Release 8
- GSM RRC Connection Release with Redirection without Sys Info Release 8
- RRC Connection Release with Redirection with Sys Info Release 9
- Cell change order without NACC Release 8
- Cell change order with NACC Release 8
- PS handover Release 8
- cdma2000 (1xRTT) RRC Connection Release with Redirection Release 8
- enhanced 1xCSFB Release 9
- enhanced 1xCSFB with concurrent HRPD handover Release 9
- dual receiver 1xCSFB (RRC Connection Release without Release 9 Redirection)
CS Fallback to UMTS
CS Fallback to UMTS is quite often done with RRC Connection Release with redirection info. In this case RRC Connection release message contains the target UTRAN frequency information. Then the UE moves to the target RAT and searches for an acceptable cell by utilizing the frequency information within the RRC Connection Release. Once target cell is located it starts from IDLE and obtains required system information blocks to access the cell. This solution was recommended in 3GPP Release 8.
CS Fallback to GSM
Like CS fallback to UMTS, RRC Connection Release with redirection information is the least-effort solution for CS fallback to GSM. In this solution, the UE RRC Connection in the LTE system is released and the UE is redirected to the GSM system to set up the CS service like CS fallback to UMTS. In this redirection information, the eNodeB can indicate a target frequency. Then the UE moves to the target RAT and searches for a suitable cell by using the frequency information in the RRC Connection Release. Once the UE finds a suitable cell, it starts from IDLE and acquires the necessary system information blocks to access the cell.
I have written another analysis on LTE Circuit Switched Fallback (CSFB) Performance which provides complete picture of CSFB real world results.

Permalink